Asociación entre el tiempo de enfermedad previo a broncoscopia y tiempo de alta posbroncoscopia en pacientes pediátricos con aspiración de cuerpo extraño: estudio de cohorte retrospectivo en un centro de referencia peruano, 2014-2019.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17843/rpmesp.2023.404.12977Palabras clave:
Aspiración Respiratoria, Manejo de la Vía Aérea, Pediatría, Hospitalización, PerúResumen
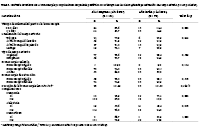
Objetivos. Determinar la asociación entre el tiempo de enfermedad previa a broncoscopia y el tiempo de alta
posbroncoscopia en pacientes pediátricos con aspiración de cuerpo extraño. Materiales y métodos. Estudio de cohorte retrospectivo. El estudio y la revisión de historias clínicas se realizaron en el Hospital de Emergencias Pediátricas de Lima, Perú. Se revisaron 324 historias clínicas, de las cuales, 183 historias fueron seleccionadas para contar con diagnóstico de cuerpo extraño en vías aéreas y estar adecuadamente llenas. Para el análisis bivariado se utilizó la prueba exacta de Fisher y U de Mann Whitney, mientras que para el cálculo del Riesgo Relativo (RR) y su respectivo intervalo de confianza (IC) al 95% se utilizó regresión de Poisson. Resultados. Se incluyeron 183 pacientes, de los cuales, el 65,6% fueron hombres con una media de 2,4 años. La localización más frecuente fue el árbol bronquial derecho y cuerpo extraño de material orgánico. La mayoría (72,7%) de los pacientes tuvieron una alta temprana antes de las 24 horas. Se encontró una asociación entre el tiempo de enfermedad previa a la broncoscopia y el tiempo alta posbroncoscopia (RR: 2,94, IC 95%: 1,72-5,01). Conclusiones. Existe una asociación estadísticamente significativa entre el tiempo de enfermedad previa a la broncoscopia y el tiempo de estancia hospitalaria posextracción del cuerpo extraño al ajustar por edad, sexo tipo de cuerpo extraño y maniobra de boca como medida de rescate. Este hallazgo es relevante debido a que pone en evidencia la importancia de una atención temprana, diagnóstico oportuno y manejo precoz en el paciente pediátrico.
Descargas
Referencias
Sjogren PP, Mills TJ, Pollak AD, Muntz HR, Meier JD, Grimmer JF. Predictors of complicated airway foreign body extraction. Laryngoscope. 2018;128(2):490–5. doi: 10.1002/lary.26814.
Joao AB, Bueno FG. Foreign body aspiration in children. Pediatric Respiratory Reviews. 2002;3(4):303-7. doi: 10.1016/S1526-0542(02)00265-8.
Yanowsky-Reyes G, Aguirre-Jauregui OM, Trujillo Ponce SA, Rodriguez Franco E, Monroy Martín Y, Pérez Liñán JA, et al. Ingestión de sustencias químicas en esófago, análisis de las complciaciones tempranas y tardias en el manejo de los mismos, una revisión de 70 casos. iMedPub. 2013;9(2):1–7. doi: 10.3823/092.
Gómez Cervantes M, de la Torre Ramos CA, Jiménez Gómez J, Encinas Hernández JL, Hernández Oliveros F, Dore Reyes M, et al. Sospecha de aspiración de cuerpos extraños en pacientes pediátricos: Nuestra experiencia en 10 años. Cir Pediatr. 2018;31(2):81–4.
Cassol V, Marques Pereira A, Zorxela L, Michelin Becker M, Menna Barreto SS. Foreign body in children-s airways. J Pneumologia. 2003;29(3):139-44. doi: 10.1590/S0102-358620030000300005.
Tomaske M, Gerber AC, Weiss M. Anesthesia and periinterventional morbidity of rigid bronchoscopy for tracheobronchial foreign body diagnosis and removal. Paediatr Anaesth. 2006;16(2):123–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2005.01714.x.
Xu Y, Ren HB, Jiang L, Wang SF, Feng RL, Li Q. Analysis of related factors for the retention time of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in pediatrics. J Surg Res. 2019;233(72):262–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2018.08.024.
Hidaka H, Obara T, Kuriyama S, Kurosawa S, Katori Y, Kobayashi T. Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for prolonged pulmonary recovery in children from aspirated foreign body. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;77(10):1677–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl/2013.07.024.
Suzen A, Karakus SC, Erturk N. The role of flexible bronchoscopy accomplished through a laryngeal mask airway in the treatment of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019; 117:194–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.12.006.
Llanos Zavalaga L, Orellana Vasquez A, Aguado Taquire HF. Evaluación inicial del Sistena de Referencia y Contrareferencia ambulatoria en la DIRIS Lima Norte. Rev Med Hered. 2021;32(2):91-102. doi: 10.20453/rmvh.v32i3.3982.
Organización Mundial de la Salud. Módulos Nuevos [Internet]. OMS; 2018 [citado el 5 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.paho.org/es/documentos/oms-programa-orientacion-salud-adolescente-para-proveedores-salud.
Hospital de Emergencias Pediátricas [Internet]. Lima: HEP; 2023 [citado el 5 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: http://www.hep.gob.pe.
Liu B, Ding F, An Y, Li Y, Pan Z, Wang G, et al. Occult foreign body aspirations in pediatric patients: 20-years of experience. BMC Pulm Med. 2020;20(1):320. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01356-8.
Chung MK, Jeong HS, Ahn KM, Park SH, Cho JK, Son YI, et al. Pulmonary recovery after rigid bronchoscopic retrieval of airway foreign body. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(2):303-7. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000250788.93900.ef.
Cevik M, Gókdemir MT, Boleken ME, Sogut O, Kurkcuoglu C. The characteristics and outcomes of foreign body ingestion and aspiration in children due to lodged foreign body in the aerodigestive tract. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2013;29(1):53-7. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e31827b5374.
Zhong B, Sun SL, Du JT, Deng D, Liu F, Liu YF, et al. Risk factors for lower respiratory tract infection in children with tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(10):e14655. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014655.
Göktas O, Snidero S, Jahnke V, Passali D, Gregori D. Foreign body aspiration in children: Field report of a German hospital. Pediatr Int. 2010;52:100-3. doi: 10.1111.j.1442-200X.2009.02913.x.
Boufersaoui A, Smati L, Benhalla KN, Boukari R, Smail S, Anik K, et al. Foreign body aspiration in children: Experience from 2624 patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;77(10):1683-8. doi: 10.1016/j/ijporl/2013.07.026.
Shlizerman L, Mazzawi S, Rakover Y, Ashkenazi D. Foreign body aspiration in children: the effects of delayed diagnosis. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010; 31:320-24. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto/2009.03.007.
He S, Zuo ZL. Different anatomical sites of the foreign body injury with 2999 children during 2012-2016. Chin J Traumatol. 2018;21(6):333-337. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2018.07.004.
Antón-Pacheco JL, Martín-Alelú R, López M, Morante R, Merino-Mateo L, Barrero S, et al. Foreign body aspiration in children: Treatment timing and related complications. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2021;15(5)144:110690. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.110690.
Pan H, Lu Y, Shi L, Pan X, Li L, Wu Z. Similarities and differences in aspirated tracheobronchial foreign bodies in patients under the age of 3 years. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;16(4):911-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl/2012.02.002.
Cutorone C, Pedruzzi B, Tava G, Emanuelli E, Barion U, Fischetto D, et al. The complimentary role of diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopy in foreign body aspiration in children. Int J Ped Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;75(12):1481–5. doi: 10.1016/j/ijporl/2011.08.014.
Sih T, Bunnag C, Ballali S, Lauriello M, Bellussi L. Nuts and seed: a natural yet dangerous foreign body. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;14(76):S49-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.02.012.
Chung MK, Jeong HS, Ahn KM, Park SH, Cho JK, Son YI, et al. Pulmonary recovery after rigid bronchoscopic retrieval of airway foreign body. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(2):303-7. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000250788.93900.ef.
Nguyen DK, Friedlander S, Fleischman RJ, Zangwill KM. Length of Stay and Complications Associated with Febrile Infants <90 Days of Age Hospitalized in the United States, 2000-2012. Hosp Pediatr. 2018;8(12):746-752. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2018-0132.
Rance A, Mittaine M, Michelet M, Martin Blondel A, Labouret G. Delayed diagnosis of foreign body aspiration in children. Arch Pediatr. 2022;29(6):424-428. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2022.05.006.
Johnson K, Linnaus M, Notrica D. Airway foreign bodies in pediatric patients: anatomic location of foreign body affects complications and outcomes. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33(1):59-64. doi: 10.1007/s00383-016-3988-9.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Esteban Andrés Huarhua Jimenez, Alejandro Kruchinsky Lozada, Marcelo Galdos Bejar, Nilton Yhuri Carreazo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.




























