Desarrollo de la tropomiosina A recombinante antigénica de Echinococcus granulosus en un sistema bacteriano como candidato vacunal contra la equinococosis canina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17843/rpmesp.2024.414.13854Palabras clave:
ADN recombinante, equinococosis, Echinococcus granulosus, Tropomiosina, VacunaResumen
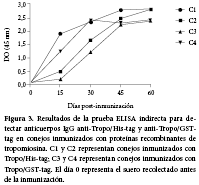
El objetivo de este estudio fue clonar, expresar y producir la proteína recombinante tropomiosina isoforma A de Echinococcus granulosus (EgTrpA) que mantenga sus propiedades antigénicas e inmunogénicas como posible candidata a vacuna para perros y ovejas. El gen de la proteína tropomiosina de Echinococcus granulosus (EgTrp), se clono en dos vectores: Tropo/His-tag [pET28a (+)] y Tropo/GST-tag (pGEX6P-1). Luego, se expresó en E. coli BL21. La identidad de la proteína se determinó mediante electroforesis bidimensional. La inmunogenicidad y la antigenicidad se verificó mediante la inmunización de conejos con cada proteína recombinante y se evaluó mediante Western Blot y ELISA. La electroforesis bidimensional identificó la proteína recombinante EgTrp como isoforma A. Las proteínas recombinantes mostraron reacciones de reconocimiento en el Western Blot y el suero de los conejos inmunizados mostró un aumento de los anticuerpos IgG de Tropo/His-tag similar a Tropo/GST-tag. La proteína recombinante EgTrpA demostró características antigénicas e inmunogénicas en animales de laboratorio.
Descargas
Referencias
Thompson RCA. The Molecular Epidemiology of Echinococcus Infections. Pathogens. 2020;9(6):453. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9060453.
Craig PS, McManus DP, Lightowlers MW, Chabalgoity JA, Garcia HH, Gavidia CM, et al. Prevention and control of cystic echinococcosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(6):385-394. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70134-2.
Chrieki M. Echinococcosis--an emerging parasite in the immigrant population. Am Fam Physician. 2002;66(5):817-820.
Craig P, Mastin A, van Kesteren F, Boufana B. Echinococcus granulosus: Epidemiology and state-of-the-art of diagnostics in animals. Vet Parasitol. 2015;213(3-4):132-148. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.07.028.
Zhang W, McManus DP. Vaccination of dogs against Echinococcus granulosus: a means to control hydatid disease? Trends Parasitol. 2008;24(9):419-424. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2008.05.008.
Budke CM, Campos-Ponce M, Qian W, Torgerson PR. A canine purgation study and risk factor analysis for echinococcosis in a high endemic region of the Tibetan plateau. Vet Parasitol. 2005;127(1):43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.08.024.
Wang Y, Xiao D, Shen Y, Han X, Zhao F, Li X, et al. Proteomic analysis of the excretory/secretory products and antigenic proteins of Echinococcus granulosus adult worms from infected dogs. BMC Vet Res. 2015;11:119. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0423-8.
Zhang W, Zhang Z, Shi B, Li J, You H, Tulson G, et al. Vaccination of dogs against Echinococcus granulosus, the cause of cystic hydatid disease in humans. J Infect Dis. 2006;194(7):966-974. doi: 10.1086/506622.
Schevzov G, Vrhovski B, Bryce NS, Elmir S, Qiu MR, O’neill GM, et al. Tissue-specific tropomyosin isoform composition. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53(5):557-570. doi: 10.1369/jhc.4A6505.2005.
Petavy AF, Hormaeche C, Lahmar S, Ouhelli H, Chabalgoity A, Marchal T, et al. An oral recombinant vaccine in dogs against Echinococcus granulosus, the causative agent of human hydatid disease: a pilot study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2008;2(1):e125. 2008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000125.
Green MR, Sambrook J. Cloning and Transformation with Plasmid Vectors. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2021;2021(11):10.1101/pdb.top101170. 2021. doi: 10.1101/pdb.top101170.
Kittelberger R, Reichel MP, Jenner J, Heath DD, Lightowlers MW, Moro P, et al. Evaluation of three enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) for the detection of serum antibodies in sheep infected with Echinococcus granulosus. Vet Parasitol. 2002;110(1-2):57-76. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(02)00308-4.
Li ZJ, Zhao W. Analysis of protoscoleces-specific antigens from Echinococcus granulosus with proteomics combined with Western blot. Biomed Environ Sci. 2012;25(6):718-723. doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2012.06.015.
Schevzov G, Vrhovski B, Bryce NS, Elmir S, Qiu MR, O’neill GM, et al. Tissue-specific tropomyosin isoform composition. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53(5):557-570. doi: 10.1369/jhc.4A6505.2005.
Esteves A, Señorale M, Ehrlich R. A tropomyosin gene is differentially expressed in the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol Res. 2003;89(6):501-502. doi: 10.1007/s00436-002-0791-4.
Alvite G, Esteves A. Echinococcus granulosus tropomyosin isoforms: from gene structure to expression analysis. Gene. 2009;433(1-2):40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.11.021.
Jazouli M, Lightowlers M, Gauci CG, Tadlaoui K, Belmlih A, Ennaji MM, et al. Vaccination Against Hydatidosis: Molecular Cloning and Optimal Expression of the EG95NC- Recombinant Antigen in Escherichia coli. Protein J. 2017;36(6):472-477. doi: 10.1007/s10930-017-9742-x.
Garcia J, Santana Z, Zumalacárregui L, Quintana M, Gonzáles D, Furrazola G, et al. Estrategias de obtención de proteínas recombinantes en Escherichia coli. Vaccimonitor 2013;22(2): 30-39.
Jara LM, Rodriguez M, Altamirano F, Herrera A, Verastegui M, Gímenez-Lirola LG, et al. Development and Validation of a Copro-Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Sandwich for Detection of Echinococcus granulosus-Soluble Membrane Antigens in Dogs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019;100(2):330-335. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0645
Sanchez L, Mayta H, Jara LM, Verástegui M, Gilman RH, Gómez-Puerta LA, et al. Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto and E. canadensis are distributed in livestock of highly endemic area in the Peruvian highlands. Acta Trop. 2022;225:106178. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2021.106178.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Janet Acosta-Benites, Luis M. Jara Salazar, Manuela Verastegui Pimentell, , Faride Altamirano-Zevallos, Nicasio Valencia Mamani Valencia Mamani, Cesar M. Gavidia Chucán

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.




























